Insect and Pest Management: Essential Strategies for Modern Farming

In today's agricultural landscape, insect and pest management has become an indispensable part of farming. Effective management strategies are crucial for ensuring crop health and maximizing yield. This comprehensive guide aims to provide farmers with the knowledge and techniques necessary to combat pests effectively while promoting sustainable farming practices.
Understanding Insects and Pests
Before diving into management techniques, it is essential to understand the various types of insects and pests that can affect crops:
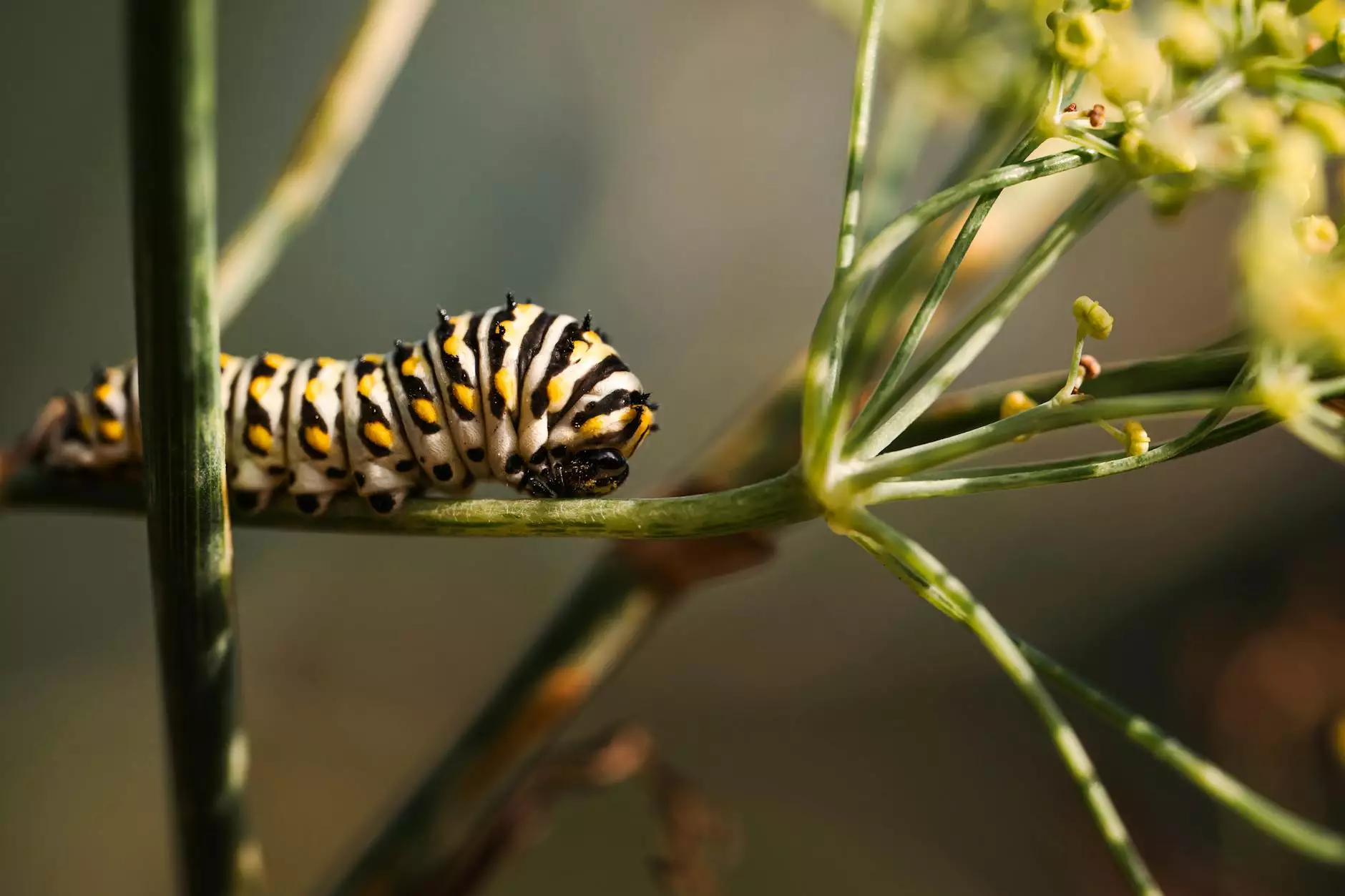
- Insects: Small arthropods, including beetles, aphids, and caterpillars, that can cause significant damage to plants.
- Rodents: Field mice and rats that can eat and destroy crops, stored grains, and feed.
- Nematodes: Microscopic worms that attack plant roots, leading to reduced nutrient uptake.
- Weeds: Although not insects, weeds compete with crops for resources and can harbor pests.
The Importance of Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
One of the most effective approaches to insect and pest management is through Integrated Pest Management (IPM). IPM combines biological, cultural, physical, and chemical tools to minimize pest damage while reducing risks to human health and the environment.
Principles of IPM
- Prevention: Implement practices that deter pests, such as crop rotation and using resistant crop varieties.
- Monitoring: Regularly check for pest presence and damage to assess pest populations accurately.
- Identification: Correctly identify pests to determine the most appropriate management methods.
- Action Thresholds: Define levels at which pest populations begin to cause economic harm, guiding when to take action.
- Control Methods: Employ a combination of biological, cultural, physical, and chemical controls as needed.
Key Strategies for Effective Insect and Pest Management
1. Biological Control
Biological control involves using natural predators or parasites to manage pest populations. This method is environmentally friendly and often sustainable.
Examples include:
- Ladybugs: Known to control aphid populations.
- Nematodes: Beneficial nematodes can target soil-dwelling pests.
- Parasitoids: Wasps that lay their eggs in or on pest insects.
2. Cultural Control
Cultural practices can reduce pest establishment, reproduction, and survival. Some effective cultural controls include:
- Crop rotation to disrupt pest life cycles.
- Sanitation practices to remove debris and potential pest habitats.
- Choosing resistant crop varieties that can withstand pest infestations.
3. Mechanical and Physical Control
Mechanical and physical methods can physically remove or exclude pests from crops. Techniques include:
- Traps: Using traps for capturing insects or rodents.
- Barriers: Floating row covers, nets, and fencing to prevent pest access.
- Handpicking: Removing pests manually from plants.
4. Chemical Control
When pests exceed action thresholds, chemical control may be necessary. However, it should be used judiciously to minimize environmental impact.
Farmers should consider:
- Choosing targeted pesticides: Use chemicals that specifically target the pest without harming beneficial organisms.
- Following label instructions: Adherence to recommended dosages and timings to maximize effectiveness and safety.
- Timing: Apply treatments when pests are most vulnerable, such as during early life stages.
Promoting Beneficial Insects
Encouraging beneficial insects on your farm can naturally control pest populations. This can be achieved through:
- Planting nectar-producing crops: Plants like marigolds and dill attract beneficial insects.
- Create habitats: Providing shelter with hedgerows or insect hotels.
- Minimizing pesticide use: Reducing exposure to non-target organisms will help maintain beneficial insect populations.
The Role of Technology in Pest Management
In recent years, technology has revolutionized insect and pest management. Here are several advancements making a significant impact:
- Precision Agriculture: Utilizing GPS and IoT devices to monitor crop health and pest presence accurately.
- Drones: These can be used for aerial imagery and pest scouting, providing timely data.
- Mobile Apps: Dedicated applications help farmers track pest outbreaks and identify species through image recognition.
Importance of Education and Training
Continuous education and training in pest management are vital for success. Farmers should connect with local extension services for advice and resources. Engage in workshops, online courses, and community groups to stay updated on best practices.
Conclusion: A Holistic Approach to Insect and Pest Management
In summary, effective insect and pest management requires a holistic approach that combines various strategies to ensure sustainable agricultural practices. By integrating biological, cultural, mechanical, and chemical controls, farmers can enhance their crop resilience and ensure a productive yield.
As agriculture continues to evolve, it's essential to embrace technology and foster beneficial ecosystems on the farm. At TSGC Inc., we are committed to providing the necessary support and resources for farmers to thrive in managing pests effectively. Together, we can safeguard our agricultural future and promote a healthier environment.
© 2023 TSGC Inc. All rights reserved.