Surgical Tools: The Backbone of Modern Medicine
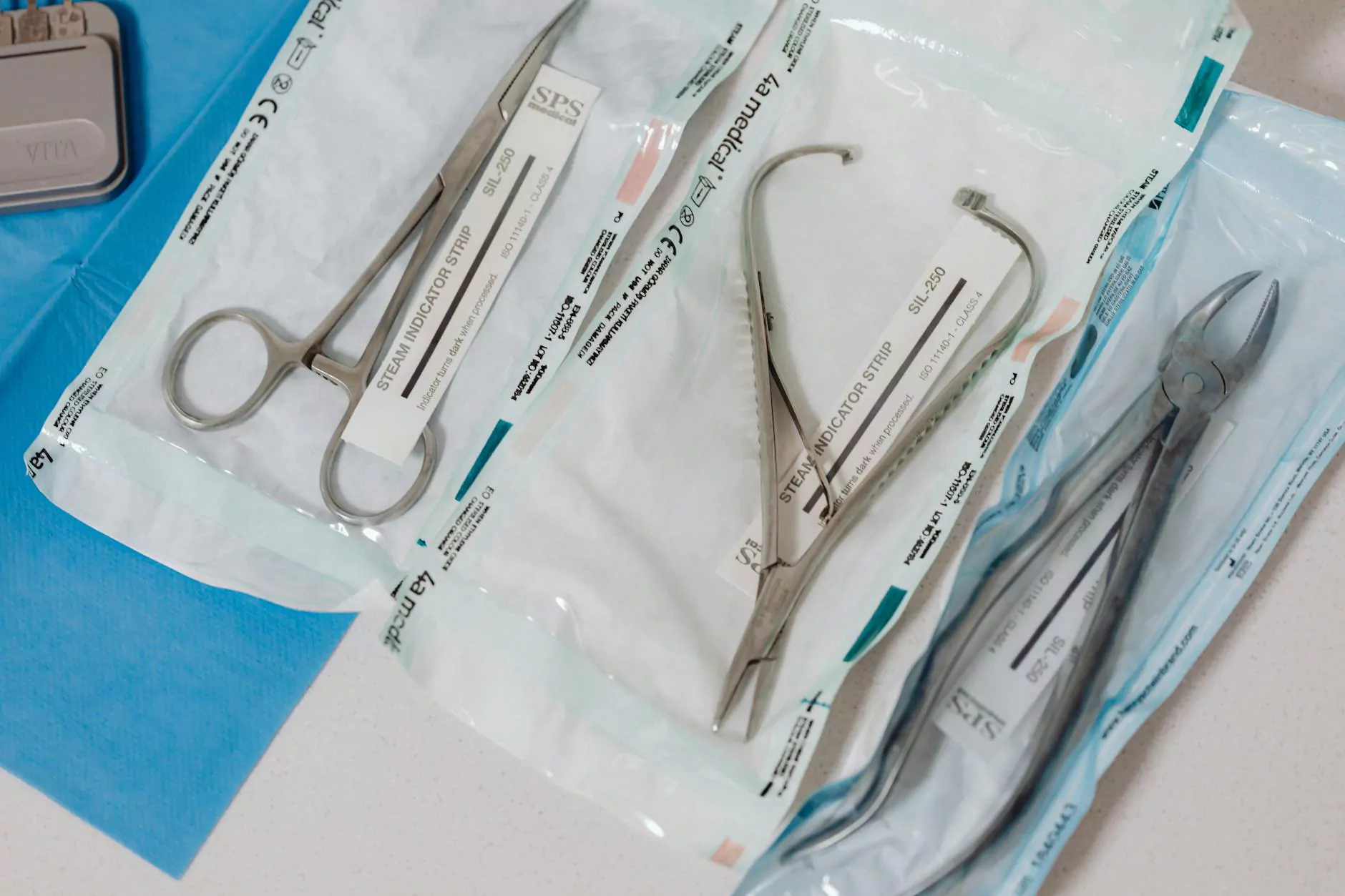
Introduction to Surgical Tools
Surgical tools are essential instruments that play a pivotal role in the realm of healthcare. These tools are designed to assist medical professionals in performing various procedures efficiently and safely. The sophisticated design and functionality of these instruments not only enhance surgical precision but also minimize the risk of complications during surgical interventions. In this article, we will delve into the different types of surgical tools, their uses, and the importance of quality in their manufacturing.
The Importance of Surgical Tools in Healthcare
The quality and efficacy of surgical procedures heavily depend on the tools utilized during operations. Surgical instruments are not just tools; they embody the advancement of medical technology. High-quality surgical instruments can:
- Increase surgical efficiency: Specialized instruments allow for quicker and more effective surgeries.
- Enhance precision: Quality tools lead to more accurate incisions and less tissue damage.
- Reduce recovery time: Minimally invasive instruments can improve patient outcomes and expedite recovery.
- Ensure safety: Properly designed tools help minimize the risk of infections and other postoperative complications.
Types of Surgical Tools
Surgical tools can be categorized based on their use in various medical procedures. Below are some of the key categories of surgical instruments:
1. Cutting Instruments
These tools are designed for cutting tissues and organs. Common examples include:
- Scalpels: Sharp knives used for incisions.
- Scissors: Used for cutting tissues.
- Scissors: Used to cut sutures and other materials, having different shapes for specific tasks.
2. Grasping Instruments
Grasping instruments help surgeons to hold and manipulate tissues. They include:
- Forceps: Tweezer-like instruments for grasping tissues.
- Tissue Forceps: Used specifically for handling soft tissue.
3. Hemostatic Instruments
These instruments control bleeding. Examples include:
- Clamps: Instruments like hemostats that are used to occlude blood vessels.
- Suture needles: Needles used for stitching wounds.
4. Sutures and Staplers
Suturing materials and staplers are used for closing incisions or wounds. Their subcategories include:
- Absorbable sutures: Sutures that dissolve over time.
- Non-absorbable sutures: Require removal after healing.
5. Accessory Instruments
These tools assist in various tasks during surgery, including:
- Needle holders: Used to hold needles while suturing.
- Retractors: Instruments that hold back tissues for better visibility.
Selecting the Right Surgical Tools
Choosing the appropriate surgical instruments is crucial for successful outcomes. Here are key considerations when selecting surgical tools:
- Specialization: Tools should be tailored to the specific procedure.
- Material quality: High-quality stainless steel is commonly preferred for durability and sterility.
- Ergonomics: Instruments should be designed for comfortable handling to reduce fatigue during long procedures.
- Manufacturer reputation: Always choose instruments from reputable manufacturers that comply with international quality standards.
The Evolution of Surgical Tools
The history of surgical tools dates back to ancient civilizations. Understanding this evolution provides insight into modern surgical practices:
Ancient Surgical Instruments
Early instruments were fashioned from materials like bronze, stone, and wood. Basic tools such as scalpels and forceps were developed, laying the foundation for modern tools.
Medieval Advancements
The Middle Ages saw the introduction of more refined instruments, partly due to the works of scholars and anatomists who studied the human body. Instruments became more scientific, and their designs improved for better functionality.
Modern Surgical Technology
Today, surgical tools are engineered with high-precision technology. Innovations include:
- Robotic surgical systems: Allow for minimally invasive surgeries with precision.
- Endoscopic instruments: Used for internal surgeries with small incisions.
Quality Assurance and Maintenance of Surgical Tools
Ensuring the longevity and effectiveness of surgical tools is paramount. Proper maintenance practices include:
- Cleaning: Tools should be cleaned according to manufacturer guidelines to prevent infections.
- Sterilization: Autoclaving is commonly used to ensure instruments are free of contaminants.
- Regular inspections: Tools should be routinely checked for wear and tear to ensure they function correctly.
Conclusion: The Future of Surgical Tools
As the healthcare sector continues to evolve, so will the instruments that surgeons rely on. The future of surgical tools will be influenced by technological advancements and the ongoing quest for higher-quality care. Emerging trends may include:
- Smart surgical instruments: Equipped with sensors for real-time feedback during procedures.
- Sustainable materials: Biodegradable options may be developed to reduce medical waste.
- Enhanced ergonomics: Innovations designed to prevent strain and improve efficiency.
In conclusion, understanding the significance of surgical tools, their evolution, and their future potential enhances our appreciation of modern medicine and its capabilities. As healthcare continues to innovate, so too will the instruments that surgeons trust to perform life-saving procedures.